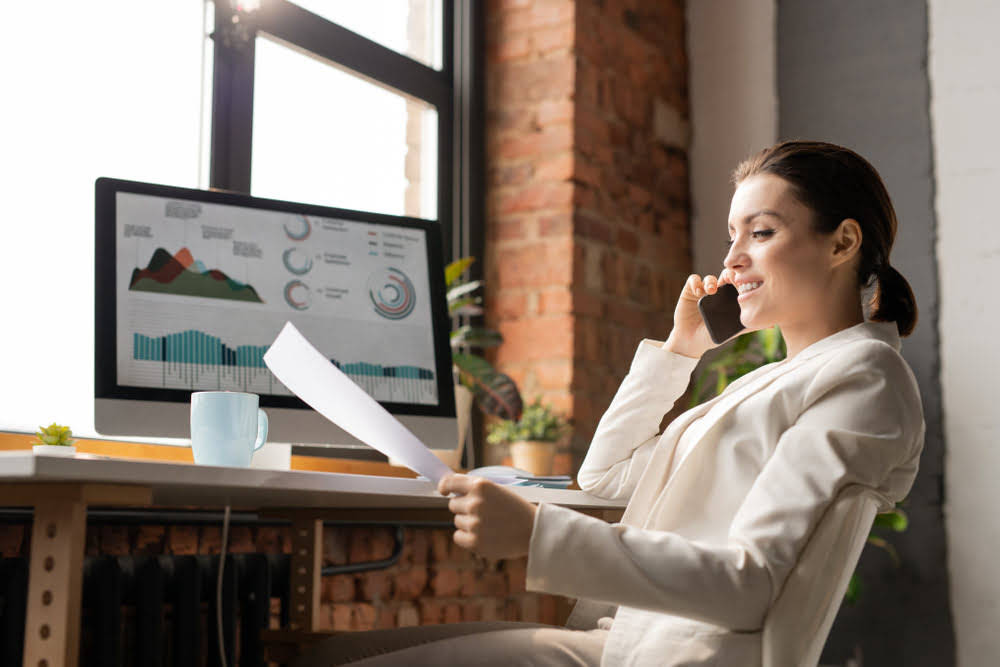
For assets themselves, liquidity is an asset’s ability to be sold without causing a significant movement in the price and with minimum loss of value. For investors and fund managers, the importance of liquidity is underscored by its role in portfolio management and risk mitigation. Highly liquid assets offer flexibility, allowing investors to adjust their portfolios in response to changing market conditions, capitalize on investment opportunities, or meet short-term liquidity needs. Additionally, liquidity provides a layer of protection against unforeseen circumstances, as it enables investors to exit positions swiftly in the event of market volatility or adverse developments.
- Unsold inventory on hand is often converted to money during the normal course of operations.
- If markets are not liquid, it becomes difficult to sell or convert assets or securities into cash.
- The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
- A balance sheet determines the financial position of your business at a particular point in time, not for a period.
- The average amount of liquidity provided through credit operations fell by €110.8 billion to €457.4 billion over the review period.
- In essence, liquidity serves as the lifeblood of financial markets, fostering efficiency, stability, and confidence among market participants.
- Similarly, for liabilities, those that are due soonest (accounts payable) are listed first, and those that are due in the longer term (deferred revenue) are listed last.
Explore everything you need to know about the concept of liquidity with our simple guide. Arranging assets and liabilities in the order of liquidity provides useful information about a company’s short-term financial health and its ability to meet its short-term obligations. These examples underscore the diverse spectrum of liquidity across asset classes, highlighting the significance of the order of liquidity in evaluating the tradability and market dynamics of different investments. Further down the order of liquidity are assets such as real estate, private equity investments, and certain types of bonds that may have limited trading activity or longer settlement periods. These assets are characterized by lower liquidity, as their conversion into cash may entail longer timeframes, transaction complexities, or the need to find suitable buyers or counterparties. There are various factors that contribute to the liquidity of an asset, including the trading volume, bid-ask spread, market depth, and the presence of willing buyers and sellers.
Liquidity
An increasing operating cash flow ratio is a sign of financial health, while those companies with declining ratios may have liquidity issues in the short-term. Cash is the most liquid asset, and companies may also hold very short-term investments that are considered cash equivalents that are also extremely liquid. Companies often have other short-term receivables that may convert to cash quickly. Unsold inventory on hand is often converted to money during the normal course of operations. Companies may also have obligations due from customers they’ve issued a credit to.
- In this article, we are going to explain the concept of order of liquidity, why companies use this method, dig into various current asset accounts and evaluate their order of liquidity and conclude with an example.
- Liquidity ratios typically compare a company’s current assets to its current liabilities to measure what short-term assets it has available to pay for its short-term debt.
- The average euro area repo rate, as measured by the RepoFunds Rate Euro index, continued to trade closer to the deposit facility rate, except around the year-end.
- An increasing operating cash flow ratio is a sign of financial health, while those companies with declining ratios may have liquidity issues in the short-term.
- Tangible assets, such as real estate, fine art, and collectibles, are all relatively illiquid.
The average euro area repo rate, as measured by the RepoFunds Rate Euro index, continued to trade closer to the deposit facility rate, except around the year-end. The repo rate was, on average, 7.3 basis points below the deposit facility rate over the review period. The 2023 end-of-year decline of 25.5 basis points was significantly less than the 226.8 basis point fall seen at the end of 2022. The average amount of liquidity provided https://www.bookstime.com/ through holdings of outright portfolios decreased by €89.3 billion over the review period. This decline was due to the discontinuation, on 1 July 2023, of reinvestments of principal payments from maturing securities under the APP. The average daily liquidity needs of the banking system, defined as the sum of net autonomous factors and reserve requirements, decreased by €104.1 billion to €1,630.9 billion over the review period.
Definition of Liquidity
Securities that are traded over the counter (OTC), such as certain complex derivatives, are often quite illiquid. For individuals, a home, a time-share, or a car are all somewhat illiquid in that it may take several weeks to months to find a buyer, and several more weeks to finalize the transaction and receive payment. Moreover, broker fees tend to be quite large (e.g., 5% to 7% on average for a real estate agent).